Wondering what grid trading is? Whether you’re a novice or an experienced trader, understanding grid trading is pivotal for strategic market navigation. In this article, you will learn what grid trading is and how it works!
Table of contents:
2. How Does Grid Trading Work?
3. Real-life Example of Grid Trading
4. Pros and Cons of Grid Trading
5. Is Grid Trading Profitable? And, Should You Use It?
6. Risk Management in Grid Trading
8. Tips for Successful Grid Trading
Ready to Practice Grid Trading Without Putting in Real Money?
What is Grid Trading?
Grid trading is a strategic approach to trading the financial markets, wherein a trader takes advantage of the natural fluctuation of prices, instead of making predictions about specific price movements. The trader divides the price range of an asset into various segments or “grids”, and sets predetermined buy and sell orders at these intervals.
Example: A trader is observing Bitcoin, a cryptocurrency whose current price is $40,000. Rather than attempting to predict its future movement, the trader sets up a grid strategy. They decide to place buy orders at every $1,000 drop and sell orders at every $1,000 rise. So, there are buy orders at $39,000, $38,000, and so on, and sell orders at $41,000, $42,000, and so forth.
If Bitcoin’s price drops to $39,000, the buy order at that price is triggered. If it then rises to $41,000, the trader sells the Bitcoin they bought at $39,000, making a $2,000 profit.
If you are new to trading, check out how to become a trader .
How Does Grid Trading Work?
Grid trading operates on a foundational principle: markets move in waves, and by capturing these oscillations, traders can profit. Instead of focusing on long-term trends or attempting to predict market tops and bottoms, grid traders set multiple orders at different price levels to capitalise on the price movements.
Choosing the Price Range:
This involves determining the highest and lowest price points between which the asset is expected to fluctuate. For instance, if a trader believes that a stock currently trading at $50 will move between $40 and $60 in the coming weeks, this becomes their range.
Determining Grid Size:
This is about deciding the number of levels or “grids” within that range. Using the above example, if the trader decides on 10 grids, there would be a $2 price range between the grid levels.
Placing Buy and Sell Orders:
For every grid level, there are predetermined buy and sell orders. Let’s continue with our stock example. If the stock drops to $48, the buy order at that level is triggered. If it subsequently rises to $52, the sell order at that level executes, securing a $4 profit per share.
Execution and Trade Management:
Active management is crucial. As the market evolves, so should the grid. This might involve adjusting the grid’s range, closing out positions manually, or even temporarily halting trading during major news events or extreme volatility.
Real-life Example of Grid Trading
Grid trading’s practicality shines when we delve into real-world scenarios. Let’s explore how this strategy might play out in the Forex trading market , specifically with the EUR/USD currency pair.
Scenario:
A trader has been observing the EUR/USD pair, noticing its volatility within a specific range. Over the past month, the pair has oscillated between 1.1800 and 1.2200. Recognising an opportunity, the trader decides to apply the grid trading strategy.
Setting Up the Grid:
The trader divides the range (1.1800 to 1.2200) into eight equal segments, resulting in a grid spacing of 0.0050. This means there will be buy orders placed at 1.1800, 1.1850, 1.1900, and upwards. Conversely, sell orders are set at intervals like 1.2200, 1.1950, 1.1900, and downwards.
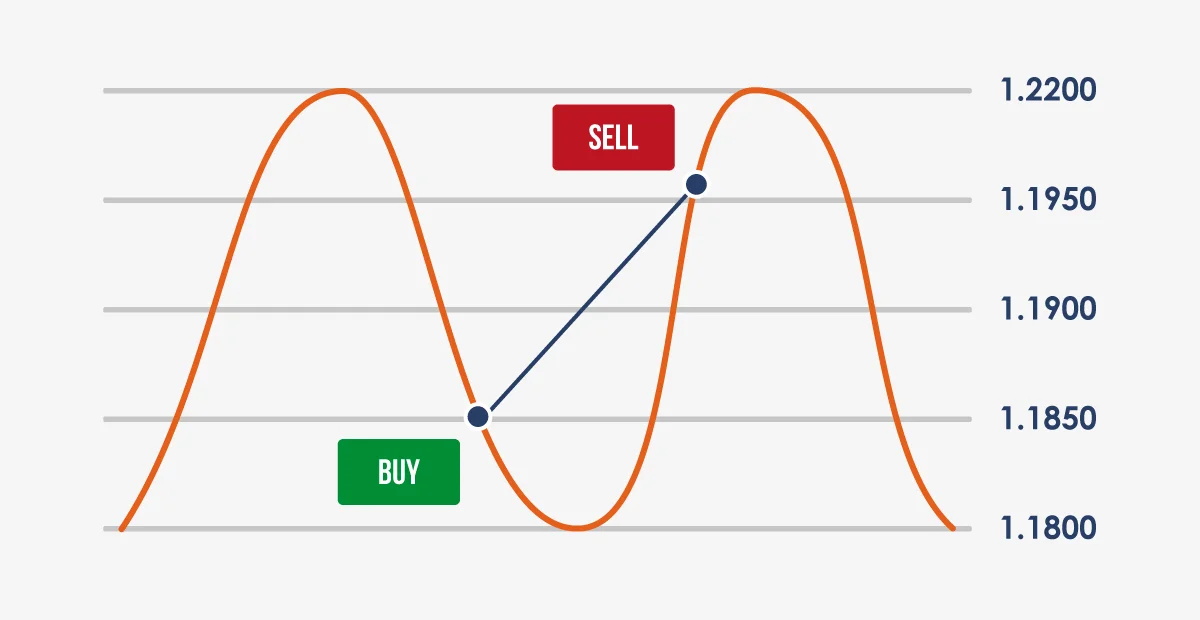
Trade Execution:
Over the next week, geopolitical events cause the EUR/USD to dip to 1.1850, triggering the buy order at that level. A few days later, positive economic data from the Eurozone pushes the pair up to 1.1950. The trader’s sell order at this level gets executed, netting a profit of 0.0100 or 100 pips.
Pros and Cons of Grid Trading
Grid trading, like any strategy, has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these can help traders make informed decisions.
3 Pros
No Need for Market Direction Prediction:
Unlike many strategies that rely on forecasting market movements, grid trading operates on the principle of price volatility. Whether the market moves up, down, or sideways, there’s always potential for profit.
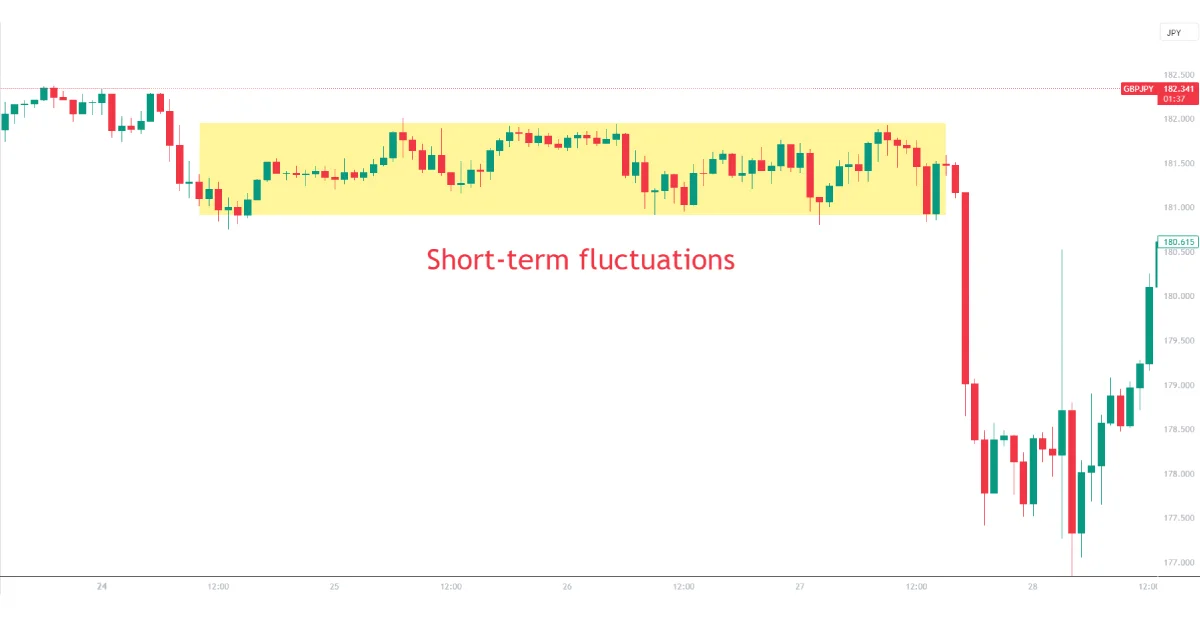
The image above shows short-term fluctuation in GBPJPY, despite the high volatility that it may experience at times.
Example: Consider the GBP/JPY pair, known for its volatility. Even if a trader is unsure of its long-term direction, they can still profit from its short-term fluctuations using grid trading.
Automation:
Many modern trading platforms offer tools or bots that can automate grid trading, allowing traders to have a hands-off approach once the grid is set up. Learn more about automated vs manual trading.
Example: A trader using the MetaTrader platform can employ Expert Advisors (EAs) to manage their grid, executing trades automatically based on the predefined grid levels.
Consistent Cash Flow:
With multiple trades executing regularly, grid trading can provide a more consistent cash flow compared to strategies that wait for a single breakout or trend.
Example: If the EUR/AUD oscillates within a 200-pip range and a trader has grids every 50 pips, they could potentially execute four profitable trades within that range.
3 Cons
Significant Drawdowns:
If the market trends strongly in one direction beyond the grid’s range, it could result in multiple losing trades.
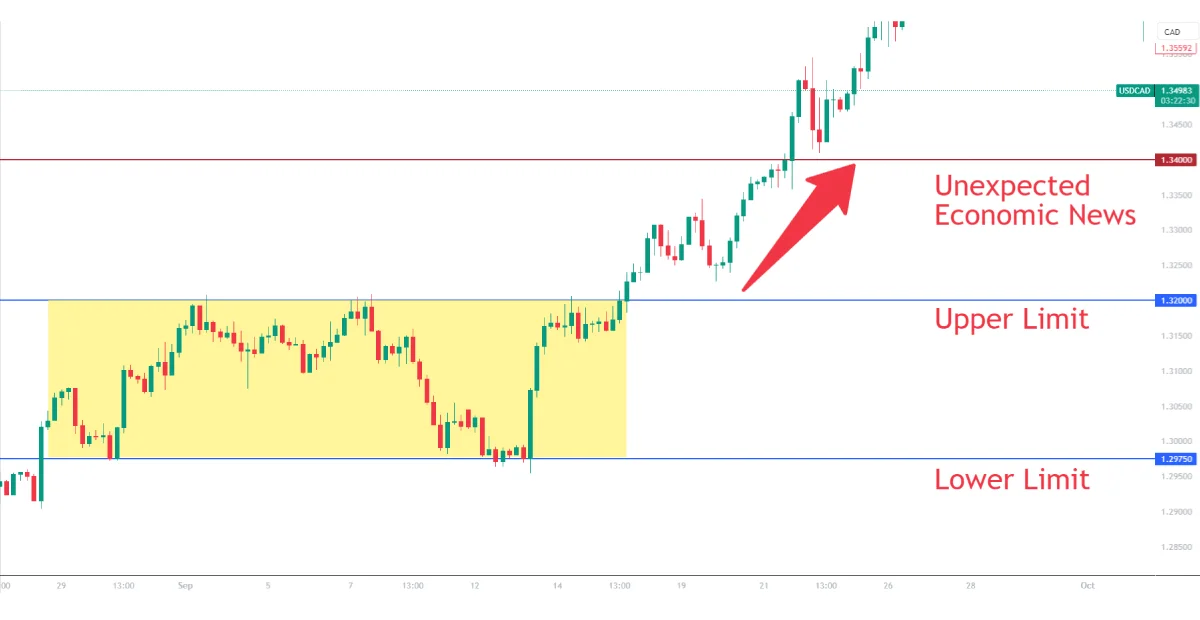
Example: If a trader sets their grid’s upper limit for the USD/CAD at 1.3200, but an unexpected economic news drives the pair to 1.3400, they could face losses on all sell orders set within the grid.
Requires Capital:
To cover multiple open positions and potential drawdowns, a substantial amount of capital might be needed, especially in highly volatile markets.
Example: Trading the volatile GBP/NZD pair with a grid strategy might require a higher capital reserve than a less volatile pair like the EUR/GBP.
Overexposure:
With multiple orders set, there’s a risk of overexposure, especially if the market moves against multiple open positions.
Example: If a trader has ten buy orders within their grid for AUD/JPY and the pair drops significantly due to an unforeseen event, all those positions could be at a loss.
Summary table
Aspect | Pros | Cons |
Market Direction | No need to predict the market’s direction. Profits from volatility regardless of market movement. | Significant drawdowns if the market moves strongly beyond the grid’s range. |
Automation | Modern platforms offer tools/bots for automated grid trading. | Requires regular monitoring to ensure automation tools are functioning as intended. |
Cash Flow | Potential for consistent cash flow due to multiple trades within the grid. | Requires substantial capital, especially in volatile markets, to cover multiple open positions. |
Exposure | Multiple entry and exit points can diversify risk. | Risk of overexposure with multiple orders, especially if the market moves against open positions. |
Is Grid Trading Profitable? And, Should You Use It?
The profitability of grid trading, like any trading strategy, hinges on various factors, including market conditions, grid setup, and risk management.
There are 3 profitability factors you need to consider :
Market Conditions:
Grid trading thrives in markets that move sideways or within a specific range. In such conditions, the strategy can consistently capture profits from the price oscillations.
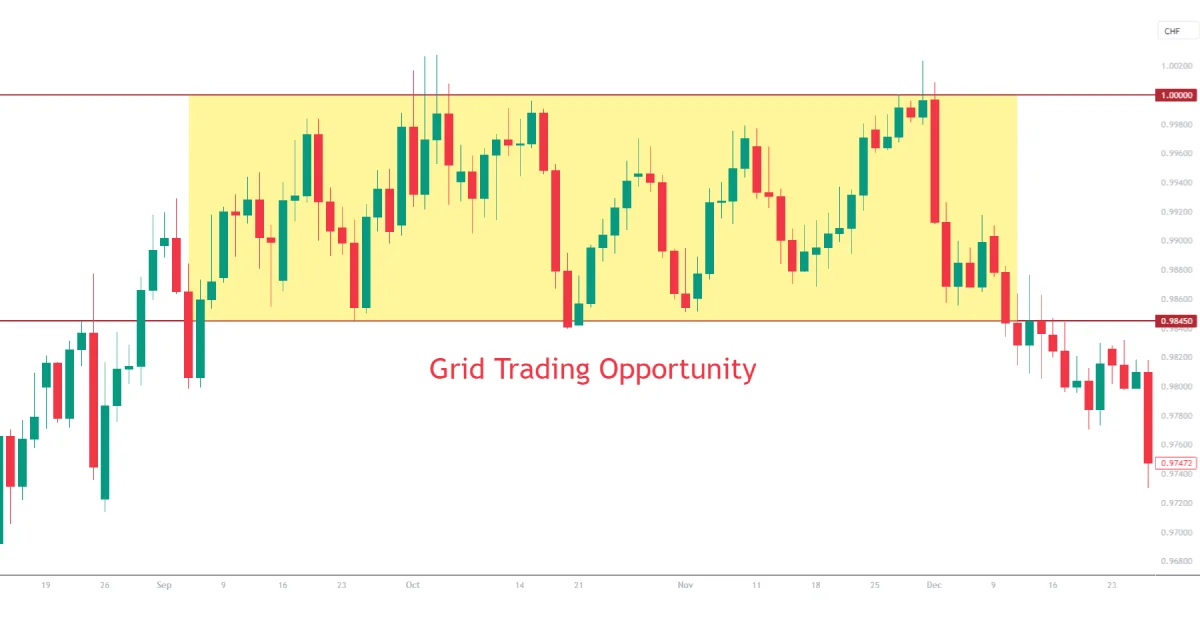
Example: In 2019, the USD/CHF pair experienced prolonged periods of range-bound movement between 0.9845 and 1.0000. A grid trader operating within this range could have capitalized on these fluctuations, making profits on both buy and sell orders.
Grid Setup:
The spacing between grid levels and the range’s width can significantly impact profitability. Tighter grids can result in more frequent trades but may also lead to quicker stop-outs in volatile conditions.
Example: If a trader sets up a grid on the EUR/USD with levels every 20 pips during a major news release, they might experience rapid trade executions but also face potential stop-outs if the news causes a sharp price spike.
Risk Management:
Effective risk management ensures that losses from unfavorable market moves don’t outweigh the profits from successful trades. Learn more about the 5 risk management techniques .
Example: A trader using grid trading on the AUD/NZD pair might set a maximum loss limit or stop-loss for each trade, ensuring that a sudden price drop doesn’t lead to significant account drawdown.
Should You Start Grid Trading ?
Grid trading isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy. While it offers unique Pros, it also comes with inherent risks. Traders should consider:
Experience Level:
Beginners might find grid trading complex, especially when manually adjusting grids in response to market changes.
Capital Availability:
The strategy often requires a substantial capital reserve to cover multiple open positions.
Risk Appetite:
Traders averse to risk might find the potential for multiple simultaneous losing positions challenging to handle.
Risk Management in Grid Trading
Effective risk management is paramount in grid trading. Given the strategy’s nature, where multiple orders can be opened simultaneously, traders must be vigilant to ensure that potential losses don’t erode their capital. There are 3 risk management techniques :
Setting Stop Losses:
This involves determining a price level where a trade will be automatically closed to prevent further losses. It’s a safety net that ensures a losing trade doesn’t drain too much capital.
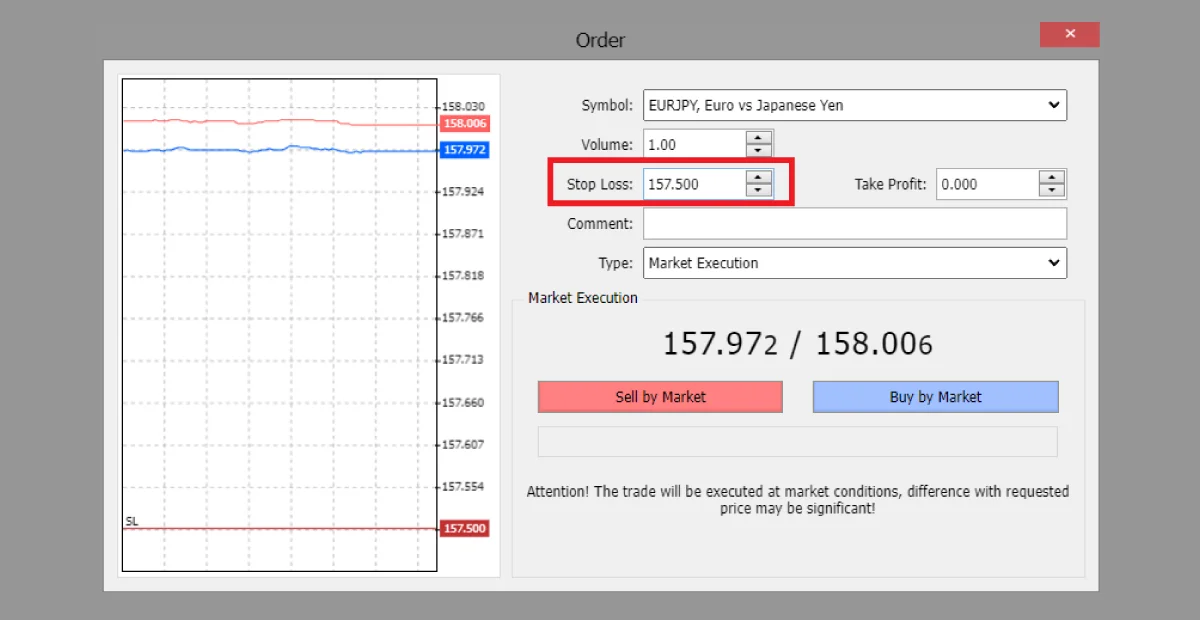
Example: A trader has a buy order for the EUR/JPY pair at 158.00. They might set a stop loss at 157.50, ensuring that if the pair moves against the trade, the loss is capped at 50 pips.
Position Sizing:
This refers to the size of the trade or the amount of capital invested in each grid level. By adjusting position sizes, traders can control their exposure and potential loss for each trade.
Example: Instead of committing 5% of their capital to each trade, a trader might decide to allocate only 2%, reducing potential losses if several trades go against them.
Hedging:
This involves taking the opposite position in a correlated asset to offset potential losses. If one trade goes south, the hedge trade might profit, balancing out the loss.
Example: A trader using grid trading on the GBP/USD might also take a position on the EUR/GBP. If the GBP strengthens, causing a loss on the GBP/USD trade, the EUR/GBP position might profit, acting as a hedge.
Platform for Grid Trading
In the realm of grid trading, the choice of platform can significantly influence a trader’s experience and profitability. Among the myriad of options available, MetaTrader 4 (MT4) stands out, especially when provided by a reputable broker like ATFX. Check out what is MT4 and how to use it .
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) by ATFX
ATFX, a globally recognized and regulated broker , offers its clients access to the renowned MetaTrader 4 platform, which is optimized for grid trading. Here’s 3 reasons why the MT4 by ATFX is a top choice for grid traders:
Customized Expert Advisors (EAs):
MT4 is known for its powerful EAs, and ATFX provides a range of customized EAs tailored for grid trading. These EAs allow traders to automate their strategies, ensuring they can capitalize on market movements even when they’re not actively monitoring the markets.
Robust Technical Analysis Tools:
MT4 boasts a comprehensive suite of technical analysis tools. With ATFX, traders get enhanced charting capabilities, allowing them to visualize their grid strategy against historical data, ensuring they set optimal grid levels. Check out the popular list of MT4 indicators provided by ATFX.
Dedicated Support:
ATFX offers dedicated customer support for its MT4 users. Whether it’s a query about the platform, an EA, or grid trading in general, ATFX’s team is ready to assist, ensuring a smooth trading experience.
Download MT4 on your device now !
Learn more about the benefits of MT4 platform .
Tips for Successful Grid Trading
Grid trading, while systematic, requires a blend of strategy, intuition, and discipline. Here are some tips to enhance your success with this approach:
Understand the Market Environment:
Grid trading is most effective in range-bound markets. Before setting up a grid, analyze the market to ensure it’s not trending strongly in one direction.
Set Clear Entry and Exit Points:
Define your grid’s boundaries. Know where you’ll start placing orders and where you’ll stop.
Use Stop Losses:
While grid trading inherently involves multiple open positions, it’s crucial to have a safety mechanism in place. Set a stop loss for each order to cap potential losses.
Regularly Review and Adjust:
The market is dynamic. Regularly review your grid strategy and make adjustments based on changing market conditions.
Stay Informed:
Keep abreast of major economic news and events. Such events can cause significant price swings, which might affect your grid strategy.
Start with a Demo Account:
Before diving into live trading account , practice grid trading on a demo account . This allows you to get a feel for the strategy without risking real funds. Learn how to use demo account to improve trading .
Many brokers, including ATFX, offer demo accounts where traders can practice strategies like grid trading in real-time market conditions without actual financial risk.
Learn more about the type of brokers – which one should you choose ?
Ready to Practice Grid Trading Without Putting in Real Money?
Dive into the world of grid trading with ATFX’s free demo account . Beyond just grid trading, ATFX offers several financial markets to explore, including the option to transition to a live account . The broker’s advanced trading platform is designed for you to test various strategies and benefit from the wealth of educational content they provide, such as trading strategies and market news. Seize this opportunity and secure your free demo trading account with ATFX now!







