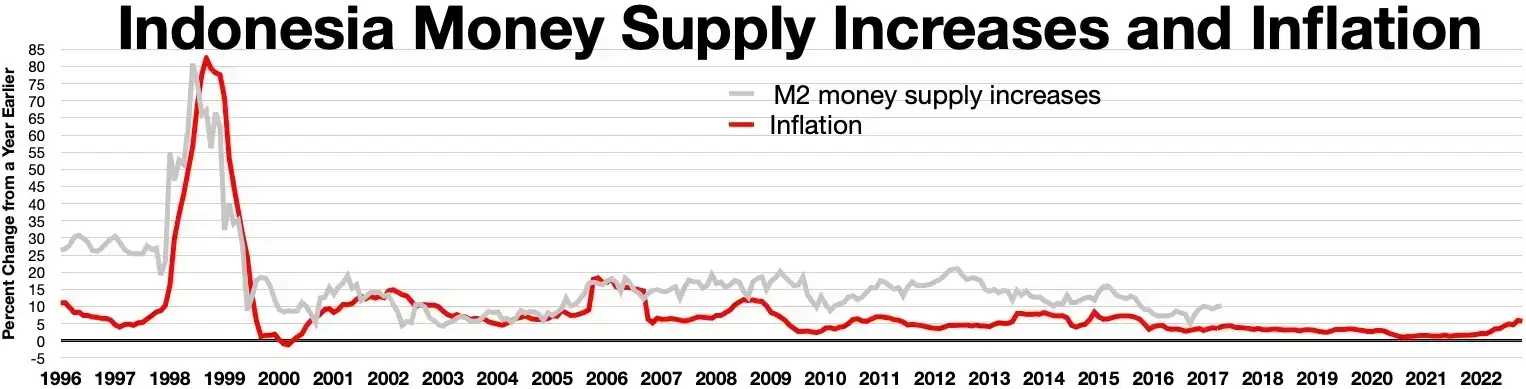
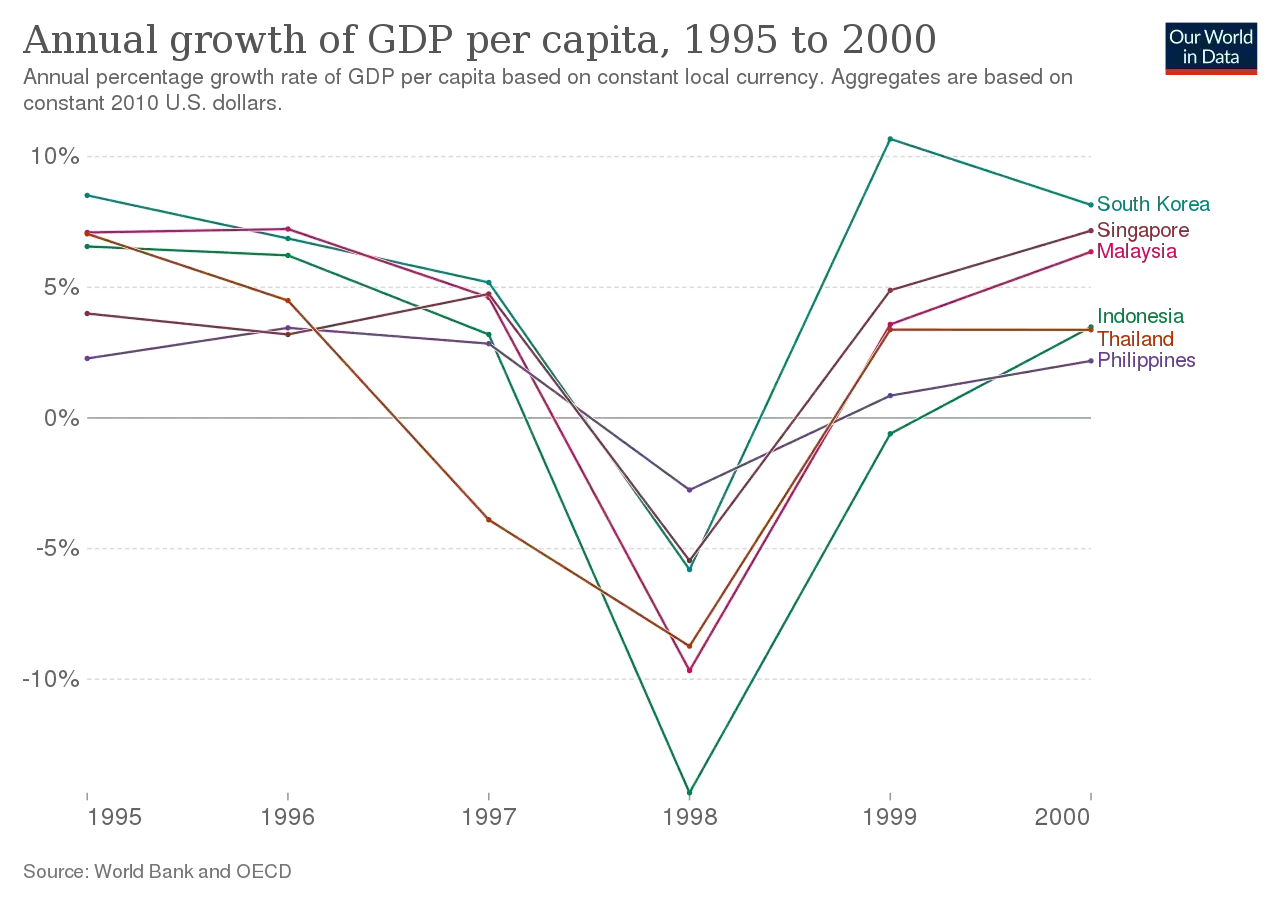
The 1997 economic crisis, also known as the Asian financial crisis, was a severe economic upheaval that affected many countries in the Asia-Pacific region, including Thailand, Indonesia, South Korea, and Malaysia. The crisis began in July 1997 and lasted several years, leading to significant economic and social disruption in the affected countries. This article will discuss the causes, impacts, and responses to the 1997 economic crisis.
Background and Context
The Asia-Pacific region had been experiencing rapid economic growth in the years leading up to the crisis, with many countries adopting market-oriented economic policies and attracting foreign investment. However, this growth was built on a foundation of financial deregulation and unsustainable lending practices, which would ultimately contribute to the crisis. Additionally, the region was heavily dependent on exports, particularly to the United States, which left it vulnerable to changes in the global economy.
1997 Asian financial crisis. (2023, February 16). Wikipedia.
6 Causes of the Crisis
The 1997 economic crisis was caused by a combination of factors:
Macroeconomic imbalances, including large current account deficits
Many affected countries, such as Thailand, Indonesia, and South Korea, had large current account deficits, which occur when a country imports more goods and services than it exports. These imbalances can lead to a loss of confidence among foreign investors, which can, in turn, trigger a currency crisis.
Overvalued currencies, which made exports less competitive
In the lead-up to the crisis, many affected countries had overvalued currencies, making their exports more expensive and less competitive in global markets. This reduced demand for their goods and services and weakened their economies.
Unsustainable lending practices
Particularly borrowing heavily from foreign lenders in the form of short-term debt. Many affected countries have borrowed heavily from foreign lenders in short-term debt, which is riskier and can lead to liquidity problems if foreign investors suddenly withdraw their funds.
Dependence on exports, particularly to the United States
Many affected countries are heavily dependent on exports, particularly to the United States. When demand for their exports declined, their economies suffered.
Withdrawal of foreign funds, leading to a shortage of liquidity
As the crisis spread, foreign investors began withdrawing their funds from affected countries, leading to a shortage of liquidity and difficulties for banks and other financial institutions.
Sharp devaluation of currencies
Leading to a surge in inflation, rise in interest rates, and collapse in asset prices: As the crisis deepened, many affected countries were forced to devalue their currencies to remain competitive. This led to a surge in inflation and interest rates, making it more difficult for businesses and households to repay their debts. The collapse in asset prices, particularly in real estate and stock markets, further weakened the economies of affected countries.
9 Impacts of the Crisis
The 1997 economic crisis profoundly impacted the affected countries with severe economic, social, and political consequences.
Sharp economic contraction and recession in affected countries
The crisis led to a sharp contraction in many affected countries’ economies, leading to a recession that lasted for several years. This led to widespread job losses and reduced economic activity.
Currency devaluations and inflation
The sharp devaluation of currencies in many affected countries led to a surge in inflation, making it more difficult for businesses and households to afford basic goods and services.

1997 Asian financial crisis. (2023, February 16). Wikipedia.
Financial sector instability and banking crises
The crisis led to a wave of financial sector instability and banking crises, as many banks and financial institutions were exposed to the risks of the crisis. This led to the collapse of many financial institutions and forced many others to be recapitalized or bailed out by governments.
Corporate bankruptcies and job losses
Many companies could not service their debts and went bankrupt, leading to job losses and reduced economic activity. This had a major impact on many industries, particularly those heavily reliant on exports.
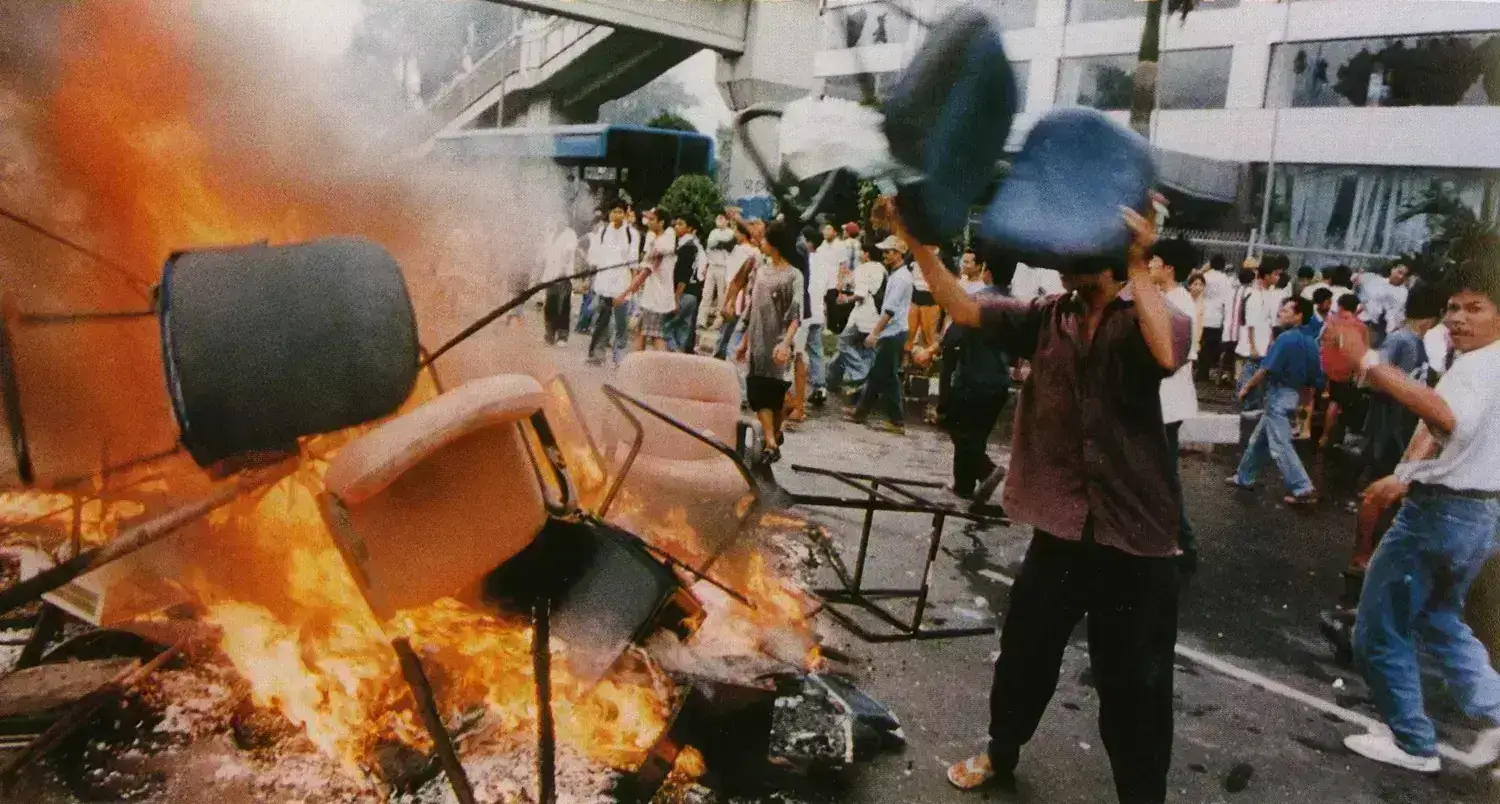
Social and political unrest
The crisis led to social and political unrest in many affected countries, as people became increasingly frustrated with the economic situation and the perceived failure of their governments to address the crisis.

1997 Asian financial crisis. (2023, February 16). Wikipedia.
Loss of investor confidence and capital flight
The crisis led to a loss of investor confidence in many affected countries, leading to capital flight and reduced investment in the affected economies.
Spillover effects on other emerging market economies
The crisis had spillover effects on other emerging market economies, particularly those with similar economic structures and vulnerabilities.
Calls for reform of international financial institutions and policies
The crisis led to calls for reform of international financial institutions and policies, particularly in the areas of financial regulation, exchange rate policy, and debt management.
Increased awareness of the risks of globalization and financial liberalization
The crisis increased awareness of the risks of globalization and financial liberalization, particularly in emerging market economies. This led to a reassessment of economic policies and greater scrutiny of the risks associated with global economic integration.
8 Responses to the Crisis
Many affected countries implemented various policies, including
International Monetary Fund (IMF) assistance
The IMF provided financial assistance to many affected countries to stabilize their economies and support reforms.
Exchange rate adjustments
Many affected countries adjusted their exchange rates to restore competitiveness and reduce the risk of currency crises.
Banking sector reforms
Many affected countries implemented reforms to strengthen their banking sectors and improve regulation and supervision.
Fiscal consolidation
Many affected countries implemented measures to reduce their budget deficits and improve their fiscal positions to restore investor confidence and reduce the risk of future crises.

1997 Asian financial crisis. (2023, February 16). Wikipedia.Debt restructuring
Many affected countries undertook debt restructuring efforts to reduce their debt burdens and make their debt more sustainable.
Trade liberalization
Some affected countries implemented trade liberalization measures to improve their competitiveness and promote economic growth.
Calls for greater international cooperation and coordination
The crisis called for greater international cooperation and coordination to better manage financial risks and promote economic stability.
Public protests and social movements
The crisis also led to public protests and social movements in many affected countries, as people demanded greater accountability and more equitable economic policies.
Conclusion
The 1997 economic crisis was a significant event in the history of the global economy and financial system. While the immediate impact of the crisis was severe, many affected countries have since recovered and become important players in the global economy. However, the crisis also left a lasting legacy, particularly regarding the importance of financial regulation and the need to address macroeconomic imbalances.
Understand Economic Events Better with Demo Account
Are you looking to better understand how economic events impact the financial markets? Open a demo account today and get hands-on experience without risking any of your hard-earned money. ATFX offers all the major financial products on a solid trading platform to practice different strategies while still learning from a guide or the free training materials ATFX provides. So, get your demo trading account for free now !